Abstract
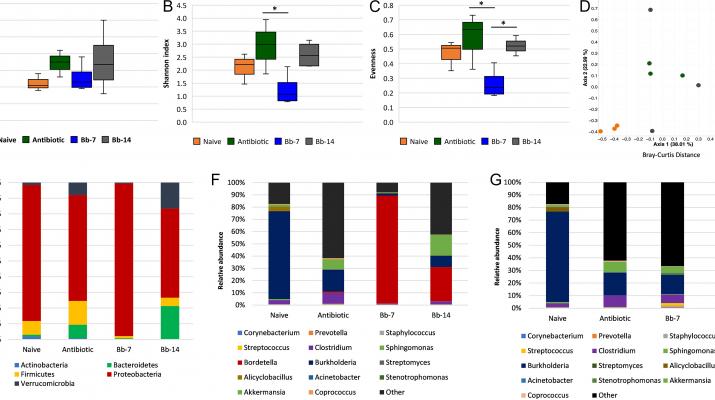
Colonization resistance, also known as pathogen interference, describes the ability of a colonizing microbe to interfere with the ability of an incoming microbe to establish infection, and in the case of pathogenic organisms, cause disease in a susceptible host. Furthermore, colonization-associated dysbiosis of the commensal microbiota can alter host immunocompetence and infection outcomes. Here, we investigated the role of Bordetella bronchiseptica nasal colonization and associated disruption of the nasal microbiota on the ability of influenza A virus to establish infection in the murine upper respiratory tract. Targeted sequencing of the microbial 16S rRNA gene revealed that B. bronchiseptica colonization of the nasal cavity efficiently displaced the resident commensal microbiota—the peak of this effect occurring 7 days postcolonization—and was associated with reduced influenza associated-morbidity and enhanced recovery from influenza-associated clinical disease. Anti-influenza A virus hemagglutinin-specific humoral immune responses were not affected by B. bronchiseptica colonization, although the cellular influenza PA-specific CD8+ immune responses were dampened. Notably, influenza A virus replication in the nasal cavity was negated in B. bronchiseptica-colonized mice. Collectively, this work demonstrates that B. bronchiseptica-mediated pathogen interference prevents influenza A virus replication in the murine nasal cavity. This may have direct implications for controlling influenza A virus replication in, and transmission events originating from, the upper respiratory tract.
IMPORTANCE The interplay of microbial species in the upper respiratory tract is important for the ability of an incoming pathogen to establish and, in the case of pathogenic organisms, cause disease in a host. Here, we demonstrate that B. bronchiseptica efficiently colonizes and concurrently displaces the commensal nasal cavity microbiota, negating the ability of influenza A virus to establish infection. Furthermore, B. bronchiseptica colonization also reduced influenza-associated morbidity and enhanced recovery from influenza-associated disease. Collectively, this study indicates that B. bronchiseptica-mediated interference prevents influenza A virus replication in the upper respiratory tract. This result demonstrates the potential for respiratory pathogen-mediated interference to control replication and transmission dynamics of a clinically important respiratory pathogen like influenza A virus.